What Are The Major Causes Of Heel Serious Pain
03/29/2015 04:47
Overview

Heel Pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message from the body that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. The greatest incidence of heel pain is seen in middle-aged men and women. It is also seen in those who take part in regular sporting activities and those significantly overweight and on their feet a lot. Heel pain can also occur in children, usually between 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities.
Causes
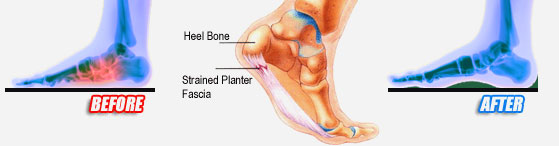
Plantar fasciitis is caused by inflammation and irritation of the tight tissue forming the arch of the foot. The most common cause of heel pain, it typically affects men, aged 40 - 70 who are physically active. The bottom or inside of the foot and / or heel (where heel and arch meet) may hurt or cause severe pain upon standing after resting -- or most often, when arising in the morning. The pain is usually experienced within the first few steps and is often characterized as "walking on nails" or knife blades. The pain may let up after walking a bit but most commonly returns after prolonged movement or a rest.
Symptoms
The primary symptom is pain in the heel area that varies in severity and location. The pain is commonly intense when getting out of bed or a chair. The pain often lessens when walking.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Clinical trials are underway investigating the use of radiofrequency to treat plantar fasciitis. It is a simple, noninvasive form of treatment. It allows for rapid recovery and pain relief within seven to 10 days. The radio waves promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) in the area. Once again, increasing blood flow to the damaged tissue encourages a healing response. Antiinflammatory medications are sometimes used to decrease the inflammation in the fascia and reduce your pain. Studies show that just as many people get better with antiinflammatories as those who don't have any improvement. Since these medications are rarely used alone, it's difficult to judge their true effectiveness. A cortisone injection into the area of the fascia may be used but has not been proven effective. Studies show better results when ultrasound is used to improve the accuracy of needle placement. Cortisone should be used sparingly since it may cause rupture of the plantar fascia and fat pad degeneration and atrophy, making the problem worse. Botulinum toxin A otherwise known as BOTOX has been used to treat plantar fasciitis. The chemical is injected into the area and causes paralysis of the muscles. BOTOX has direct analgesic (pain relieving) and antiinflammatory effects. In studies so far, there haven't been any side effects of this treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Prevention
Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.

Heel Pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message from the body that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. The greatest incidence of heel pain is seen in middle-aged men and women. It is also seen in those who take part in regular sporting activities and those significantly overweight and on their feet a lot. Heel pain can also occur in children, usually between 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is caused by inflammation and irritation of the tight tissue forming the arch of the foot. The most common cause of heel pain, it typically affects men, aged 40 - 70 who are physically active. The bottom or inside of the foot and / or heel (where heel and arch meet) may hurt or cause severe pain upon standing after resting -- or most often, when arising in the morning. The pain is usually experienced within the first few steps and is often characterized as "walking on nails" or knife blades. The pain may let up after walking a bit but most commonly returns after prolonged movement or a rest.
Symptoms
The primary symptom is pain in the heel area that varies in severity and location. The pain is commonly intense when getting out of bed or a chair. The pain often lessens when walking.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Clinical trials are underway investigating the use of radiofrequency to treat plantar fasciitis. It is a simple, noninvasive form of treatment. It allows for rapid recovery and pain relief within seven to 10 days. The radio waves promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) in the area. Once again, increasing blood flow to the damaged tissue encourages a healing response. Antiinflammatory medications are sometimes used to decrease the inflammation in the fascia and reduce your pain. Studies show that just as many people get better with antiinflammatories as those who don't have any improvement. Since these medications are rarely used alone, it's difficult to judge their true effectiveness. A cortisone injection into the area of the fascia may be used but has not been proven effective. Studies show better results when ultrasound is used to improve the accuracy of needle placement. Cortisone should be used sparingly since it may cause rupture of the plantar fascia and fat pad degeneration and atrophy, making the problem worse. Botulinum toxin A otherwise known as BOTOX has been used to treat plantar fasciitis. The chemical is injected into the area and causes paralysis of the muscles. BOTOX has direct analgesic (pain relieving) and antiinflammatory effects. In studies so far, there haven't been any side effects of this treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.
